二叉树(binary tree)是树的一种特殊形式。二叉,顾名思义,这种树的每个节点最多有2个孩子节点。注意,这里是最多有2个,也可能只有1个,或者没有孩子节点。
代码定义:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
private static class TreeNode {
int data;
TreeNode leftChild;
TreeNode rightChild;
public TreeNode(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
|
深度优先遍历
递归遍历
前序遍历
二叉树的前序遍历,输出顺序是根节点、左子树、右子树。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
public static void preOrderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
System.out.print(root.data + " ");
preOrderTraversal(root.leftChild);
preOrderTraversal(root.rightChild);
}
|
中序遍历
二叉树的中序遍历,输出顺序是左子树、根节点、右子树。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
public static void inOrderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
inOrderTraversal(root.leftChild);
System.out.print(root.data + " ");
inOrderTraversal(root.rightChild);
}
|
后序遍历
二叉树的后序遍历,输出顺序是左子树、右子树、根节点。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
public static void postOrderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
postOrderTraversal(root.leftChild);
postOrderTraversal(root.rightChild);
System.out.print(root.data + " ");
}
|
辅助栈遍历
其实二叉树遍历这里,辅助栈遍历才是重点!!!
前序遍历
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
public static void preOrderTraversalWithStack(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode p = root;
while (p != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
while (p != null) {
System.out.print(p.data + " ");
stack.push(p);
p = p.leftChild;
}
if (!stack.isEmpty()) {
p = stack.pop();
p = p.rightChild;
}
}
}
|
中序遍历
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
public static void inOrderTraversalWithStack(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode p = root;
while (p != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
while (p != null) {
stack.push(p);
p = p.leftChild;
}
if (!stack.isEmpty()) {
p = stack.pop();
System.out.print(p.data + " ");
p = p.rightChild;
}
}
}
|
后序遍历
辅助栈后序遍历难点在于遍历时需要判断当前节点是否属于右子树。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
public static void postOrderTraversalWithStack(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode p = root;
TreeNode pre = null;
while (p != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
while (p != null) {
stack.push(p);
p = p.leftChild;
}
p = stack.peek();
if (p.rightChild == null || p.rightChild == pre) {
stack.pop();
System.out.print(p.data);
pre = p;
p = null;
} else {
p = p.rightChild;
}
}
}
|
Morris算法
算法介绍
Morris算法充分利用了二叉树叶子节点下的空间,从而可以在时间复杂度为O(N),空间复杂度为O(1) 的条件下,前中后序遍历二叉树(不是完全二叉树也可以使用)。
而常见的遍历二叉树的方法为递归和栈迭代,这两种方法的时间复杂度虽然也为O(N),但是空间复杂度需要O(N),因此Morris算法可以极大节省空间。
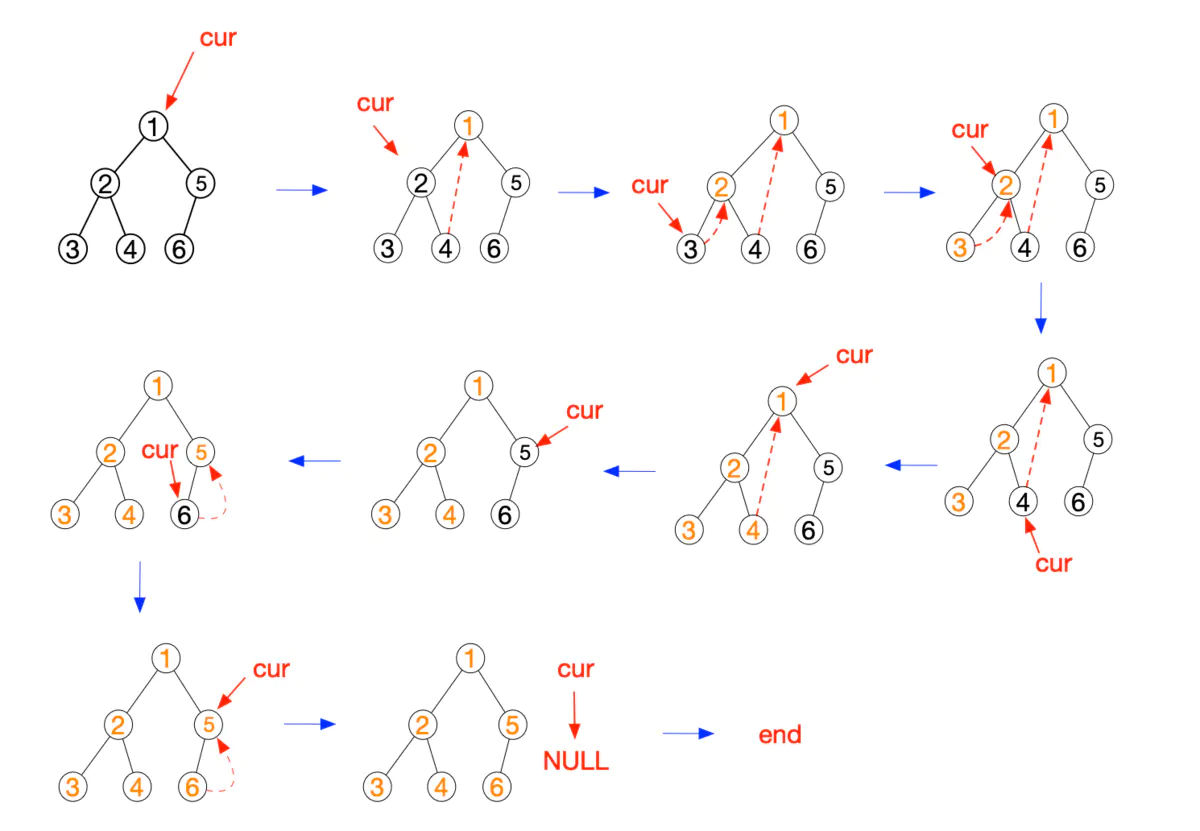
前序遍历
算法步骤
- 如果当前节点的左子节点为空时,输出当前节点,并将当前节点置为该节点的右子节点;
- 如果当前节点的左子节点不为空,找到当前节点左子树的最右节点(该节点为当前节点中序遍历的前驱节点);
- 如果最右节点的右指针为空(right=null),将最右节点的右指针指向当前节点,并输出当前节点(在此处输出),当前节点置为其左子节点;
- 如果最右节点的右指针不为空,将最右节点右指针重新置为空(恢复树的原状),并将当前节点置为其右节点;
- 重复1~2,直到当前节点为空。
图片演示
代码实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
|
public static void preOrderTraversalWithMorris(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
TreeNode cur = root;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.leftChild == null) {
System.out.print(cur.data + " ");
cur = cur.rightChild;
} else {
TreeNode t = cur.leftChild;
while (t.rightChild != null && t.rightChild != cur) {
t = t.rightChild;
}
if (t.rightChild == null) {
System.out.print(cur.data + " ");
t.rightChild = cur;
cur = cur.leftChild;
} else {
t.rightChild = null;
cur = cur.rightChild;
}
}
}
}
|
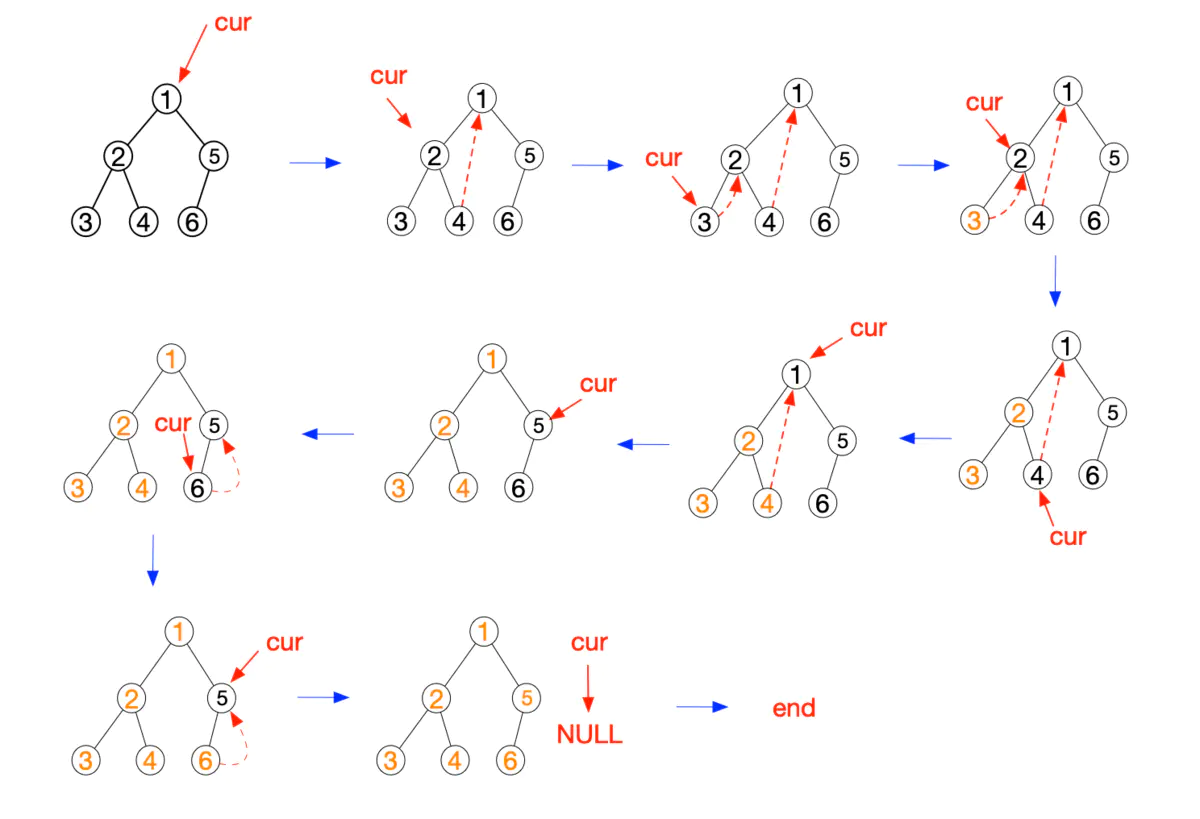
中序遍历
算法步骤
- 如果当前节点的左子节点为空时,输出当前节点,并将当前节点置为该节点的右子节点;
- 如果当前节点的左子节点不为空,找到当前节点左子树的最右节点(该节点为当前节点中序遍历的前驱节点);
- 如果最右节点的右指针为空(right=null),将最右节点的右指针指向当前节点,当前节点置为其左子节点;
- 如果最右节点的右指针不为空,将最右节点右指针重新置为空(恢复树的原状),输出当前节点,并将当前节点置为其右节点;
- 重复1~2,直到当前节点为空。
图片演示
代码实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
|
public static void inOrderTraversalWithMorris(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
TreeNode cur = root;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.leftChild == null) {
System.out.print(cur.data + " ");
cur = cur.rightChild;
} else {
TreeNode t = cur.leftChild;
while (t.rightChild != null && t.rightChild != cur) {
t = t.rightChild;
}
if (t.rightChild == null) {
t.rightChild = cur;
cur = cur.leftChild;
} else {
t.rightChild = null;
System.out.print(cur.data + " ");
cur = cur.rightChild;
}
}
}
}
|
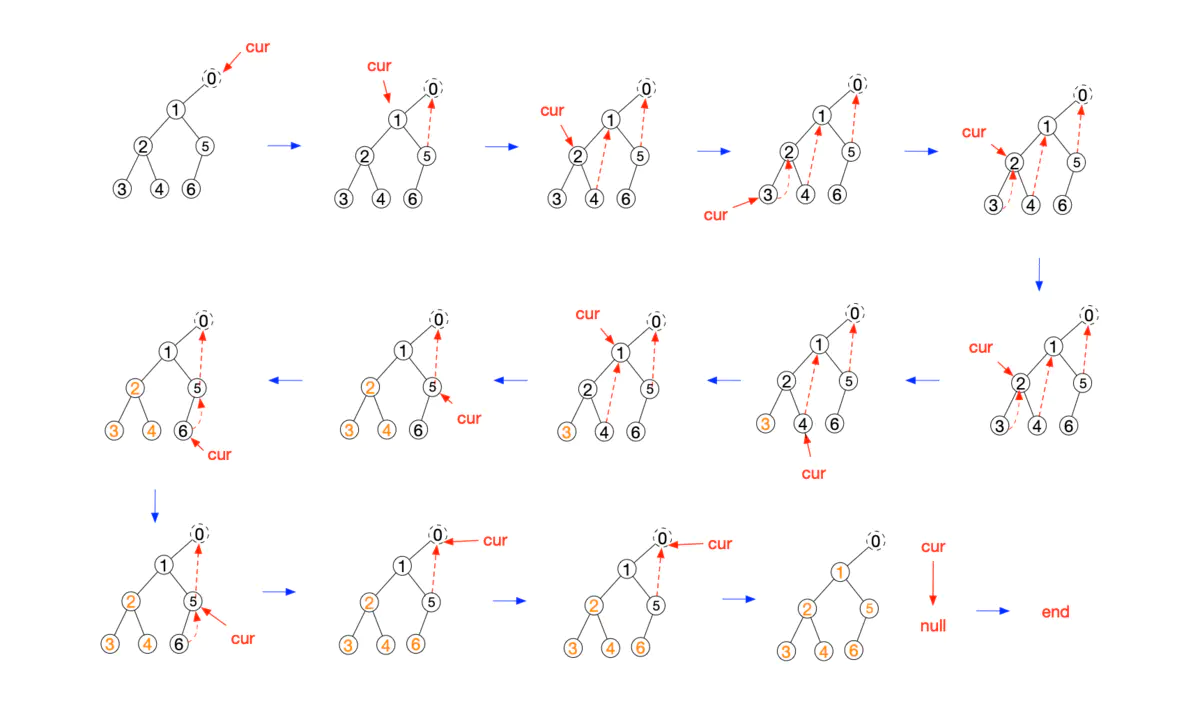
后序遍历
后序遍历较前两者比较麻烦,需要建立一个临时节点,并令该节点的左子节点为root,并且需要一个子过程,倒序输出某两个节点之间路径上的各个节点。
morris后序遍历严格意义上来说空间复杂度不为O(1)。
算法步骤
- 如果当前节点的左子节点为空时,则将其右子节点作为当前节点;
- 如果当前节点的左子节点不为空,找到当前节点左子树的最右节点(该节点为当前节点中序遍历的前驱节点);
- 如果最右节点的右指针为空(right=null),将最右节点的右指针指向当前节点,当前节点置为其左子节点;
- 如果最右节点的右指针不为空,将最右节点右指针重新置为空(恢复树的原状),倒序输出从当前节点的左子节点到该最右节点路径上的所有节点,并将当前节点置为其右节点;
- 重复1~2,直到当前节点为空。
图片演示
代码实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
|
public static void postOrderTraversalWithMorris(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
TreeNode virNode = new TreeNode(-1);
virNode.leftChild = root;
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode cur = virNode;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.leftChild == null) {
cur = cur.rightChild;
} else {
TreeNode tmp = cur.leftChild;
while (tmp.rightChild != null && tmp.rightChild != cur) {
tmp = tmp.rightChild;
}
if (tmp.rightChild == null) {
tmp.rightChild = cur;
cur = cur.leftChild;
} else {
tmp.rightChild = null;
TreeNode t = cur.leftChild;
while (t != null) {
stack.push(t);
t = t.rightChild;
}
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
System.out.print(stack.pop().data + " ");
}
cur = cur.rightChild;
}
}
}
}
|
广度优先遍历
广度优先遍历使用队列将其子节点加入队列即可。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
public static void bfs(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
LinkedList<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode r = queue.poll();
System.out.println(r.data);
if (r.leftChild != null) {
queue.offer(r.leftChild);
}
if (r.rightChild != null) {
queue.offer(r.rightChild);
}
}
}
|
参考文章:



