前言
spring框架给java工程师们提供了极大的便利,只需要添加相应的配置即可快速搭建项目骨架,将更多重心放在业务逻辑的开发中。spring具有两大核心功能:
控制反转(IoC,Inversion of Control)
传统的JAVA开发模式中,当需要一个对象时,我们使用new或者通过getInstance等直接或者间接调用构造方法创建一个对象,而在spring开发模式中,spring容器使用工厂模式为我们创建了所需要的对象,不需要我们自己去创建了,直接调用spring提供的对象就可以了,这就是控制反转。控制反转的好处有:
- 使用方便,不用开发者大量使用new
- 解耦合,实例对象交给容器管理
面向切面编程(AOP)
在面向对象编程(OOP)中,我们将事务纵向抽成一个个的对象,而在面向切面编程中,我们将一个个的对象某些类似的方面横向抽成一个切面,对这个切面进行一些如权限控制,事务管理,日志记录等公用操作处理的过程,就是面向切面编程的思想。
实现ioc
主要流程图

加载类文件
首先我们需要加载包下的类文件,包名我们可以手动配置,因此提供配置文件:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
|
public interface ConfigConstant {
String CONFIG_FILE = "wolf.properties";
String JDBC_DRIVER = "wolf.framework.jdbc.driver";
String JDBC_URL = "wolf.framework.jdbc.url";
String JDBC_USERNAME = "wolf.framework.jdbc.username";
String JDBC_PASSWORD = "wolf.framework.jdbc.password";
String APP_BASE_PACKAGE = "wolf.framework.app.base_package";
String APP_JSP_PATH = "wolf.framework.app.jsp_path";
String APP_ASSET_PATH = "wolf.framework.app.asset_path";
String APP_UPLOAD_LIMIT = "wolf.framework.app.upload_limit";
}
|
提供properties工具类:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
|
public final class PropsUtil {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(PropsUtil.class);
public static Properties loadProps(String fileName) {
Properties props = null;
InputStream is = null;
try {
is = ClassUtil.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream(fileName);
if (is == null) {
throw new FileNotFoundException(fileName + " file is not found");
}
props = new Properties();
props.load(is);
} catch (IOException e) {
LOGGER.error("load properties file failure", e);
} finally {
if (is != null) {
try {
is.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
LOGGER.error("close input stream failure", e);
}
}
}
return props;
}
public static String getString(Properties props, String key) {
return getString(props, key, "");
}
public static String getString(Properties props, String key, String defaultValue) {
String value = defaultValue;
if (props.contains(key)) {
value = props.getProperty(key);
}
return value;
}
public static int getInt(Properties props, String key) {
return getInt(props, key, 0);
}
public static int getInt(Properties props, String key, int defaultValue) {
int value = defaultValue;
if (props.contains(key)) {
value = CastUtil.castInt(props.getProperty(key));
}
return value;
}
public static boolean getBoolean(Properties props, String key) {
return getBoolean(props, key, false);
}
public static boolean getBoolean(Properties props, String key, boolean defaultValue) {
boolean value = defaultValue;
if (props.containsKey(key)) {
value = CastUtil.castBoolean(props.getProperty(key));
}
return value;
}
}
|
通过配置文件我们可以知道包名,因此也能拿到类文件的地址。接下来提供一个class工具类,主要目的为加载类,返回所有类信息。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
|
public final class ClassUtil {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ClassUtil.class);
public static ClassLoader getClassLoader() {
return Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
}
public static Class<?> loadClass(String className, boolean isInitialized) {
Class<?> cls;
try {
cls = Class.forName(className, isInitialized, getClassLoader());
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
LOGGER.error("load class failure", e);
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return cls;
}
public static Class<?> loadClass(String className) {
return loadClass(className, true);
}
public static Set<Class<?>> getClassSet(String packageName) {
Set<Class<?>> classSet = new HashSet<Class<?>>();
try {
Enumeration<URL> urls = getClassLoader().getResources(packageName.replace(".", "/"));
while (urls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = urls.nextElement();
if (url != null) {
String protocol = url.getProtocol();
if ("file".equals(protocol)) {
String packagePath = url.getPath().replaceAll("%20", " ");
addClass(classSet, packagePath, packageName);
} else if ("jar".equals(protocol)) {
JarURLConnection jarURLConnection = (JarURLConnection) url.openConnection();
if (jarURLConnection != null) {
JarFile jarFile = jarURLConnection.getJarFile();
if (jarFile != null) {
Enumeration<JarEntry> jarEntries = jarFile.entries();
while (jarEntries.hasMoreElements()) {
JarEntry jarEntry = jarEntries.nextElement();
String jarEntryName = jarEntry.getName();
if (jarEntryName.endsWith(".class")) {
String className = jarEntryName.substring(0, jarEntryName.lastIndexOf(".")).replaceAll("/", ".");
doAddClass(classSet, className);
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
LOGGER.error("get class set failure", e);
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return classSet;
}
private static void addClass(Set<Class<?>> classSet, String packagePath, String packageName) {
File[] files = new File(packagePath).listFiles(new FileFilter() {
@Override
public boolean accept(File file) {
return (file.isFile() && file.getName().endsWith(".class")) || file.isDirectory();
}
});
for (File file : files) {
String fileName = file.getName();
if (file.isFile()) {
String className = fileName.substring(0, fileName.lastIndexOf("."));
if (StringUtil.isNotEmpty(packageName)) {
className = packageName + "." + className;
}
doAddClass(classSet, className);
} else {
String subPackagePath = fileName;
if (StringUtil.isNotEmpty(packagePath)) {
subPackagePath = packagePath + "/" + subPackagePath;
}
String subPackageName = fileName;
if (StringUtil.isNotEmpty(packageName)) {
subPackageName = packageName + "." + subPackageName;
}
addClass(classSet, subPackagePath, subPackageName);
}
}
}
private static void doAddClass(Set<Class<?>> classSet, String className) {
Class<?> cls = loadClass(className, false);
classSet.add(cls);
}
}
|
生成实例对象
我们已经拿到了类的信息,因此可以实例化类并用map保存起来,实例化的对象就叫bean。并不是所有的类都需要实例化,因此提供ClassHelper,供我们筛选指定的目标,例如带有service注解的类:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
|
public final class ClassHelper {
private static final Set<Class<?>> CLASS_SET;
static {
String basePackage = ConfigHelper.getAppBasePackage();
CLASS_SET = ClassUtil.getClassSet(basePackage);
}
public static Set<Class<?>> getClassSet() {
return CLASS_SET;
}
public static Set<Class<?>> getServiceClassSet() {
Set<Class<?>> classSet = new HashSet<Class<?>>();
for (Class<?> cls : CLASS_SET) {
if (cls.isAnnotationPresent(Service.class)) {
classSet.add(cls);
}
}
return classSet;
}
public static Set<Class<?>> getControllerClassSet() {
Set<Class<?>> classSet = new HashSet<Class<?>>();
for (Class<?> cls : CLASS_SET) {
if (cls.isAnnotationPresent(Controller.class)) {
classSet.add(cls);
}
}
return classSet;
}
public static Set<Class<?>> getBeanClassSet() {
Set<Class<?>> beanClassSet = new HashSet<Class<?>>();
beanClassSet.addAll(getServiceClassSet());
beanClassSet.addAll(getControllerClassSet());
return beanClassSet;
}
public static Set<Class<?>> getClassSetBySuper(Class<?> superClass) {
Set<Class<?>> classSet = new HashSet<Class<?>>();
for (Class<?> cls : CLASS_SET) {
if (superClass.isAssignableFrom(cls) && !superClass.equals(cls)) {
classSet.add(cls);
}
}
return classSet;
}
public static Set<Class<?>> getClassSetByAnnotation(Class<? extends Annotation> annotationClass) {
Set<Class<?>> classSet = new HashSet<Class<?>>();
for (Class<?> cls : CLASS_SET) {
if (cls.isAnnotationPresent(annotationClass)) {
classSet.add(cls);
}
}
return classSet;
}
}
public final class BeanHelper {
private static final Map<Class<?>, Object> BEAN_MAP = new HashMap<Class<?>, Object>();
static {
Set<Class<?>> beanClassSet = ClassHelper.getBeanClassSet();
for (Class<?> beanClass : beanClassSet) {
Object obj = ReflectionUtil.newInstance(beanClass);
BEAN_MAP.put(beanClass, obj);
}
}
public static Map<Class<?>, Object> getBeanMap() {
return BEAN_MAP;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static <T> T getBean(Class<T> cls) {
if (!BEAN_MAP.containsKey(cls)) {
throw new RuntimeException("can not get bean by class: " + cls);
}
return (T) BEAN_MAP.get(cls);
}
public static void setBean(Class<?> cls, Object obj) {
BEAN_MAP.put(cls, obj);
}
}
|
依赖注入
上述操作我们已经把注解标注的类都实例化到bean容器中了,接下来考虑类与类的依赖关系,因此实现依赖注入。
依赖注入的主要步骤为:
- 获取类
- 判断类中是否依赖其他类
- 从bean容器中拿到依赖类注入到当前bean中
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
|
public final class IocHelper {
static {
Map<Class<?>, Object> beanMap = BeanHelper.getBeanMap();
if (CollectionUtil.isNotEmpty(beanMap)) {
for (Map.Entry<Class<?>, Object> beanEntry : beanMap.entrySet()) {
Class<?> beanClass = beanEntry.getKey();
Object beanInstance = beanEntry.getValue();
Field[] beanFields = beanClass.getDeclaredFields();
if (ArrayUtil.isNotEmpty(beanFields)) {
for (Field beanField : beanFields) {
if (beanField.isAnnotationPresent(Inject.class)) {
Class<?> beanFieldClass = beanField.getType();
Object beanFieldInstance = beanMap.get(beanFieldClass);
if (beanFieldInstance != null) {
ReflectionUtil.setField(beanInstance, beanField, beanFieldInstance);
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
|
以上就是简易版的控制反转,能够使用@Service、@Sontroller等注解管理bean,同时使用@Inject注解进行依赖注入
实现aop
主要流程图
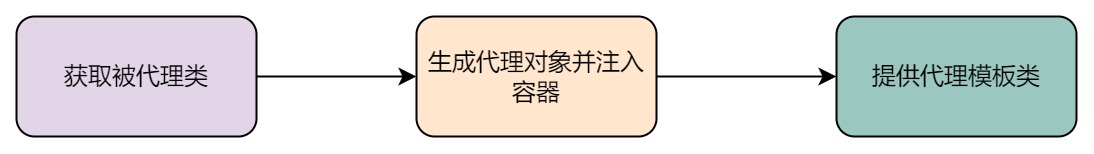
获取被代理类
为了实现切面编程,首先需要知道的就是哪些是被代理类,为了方便,我们可以使用自定义注解区分。例如被标注了@Logs的类就是我们的代理类,因此在@Aspect中,我们需要设置代理注解的值:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Aspect {
Class<? extends Annotation> value();
}
|
根据value()我们即可获取被代理类的注解。
生成代理对象
由于代理对象不止一个,因此我们要获取所有的代理对象,组成一个代理类链,并与被代理类形成映射。最终我们将被代理类信息与代理类实例注入到容器中。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
|
public final class AopHelper {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(AopHelper.class);
static {
try {
Map<Class<?>, Set<Class<?>>> proxyMap = createProxyMap();
Map<Class<?>, List<Proxy>> targetMap = createTargetMap(proxyMap);
for (Map.Entry<Class<?>, List<Proxy>> targetEntry : targetMap.entrySet()) {
Class<?> targetClass = targetEntry.getKey();
List<Proxy> proxyList = targetEntry.getValue();
Object proxy = ProxyManager.createProxy(targetClass, proxyList);
BeanHelper.setBean(targetClass, proxy);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
LOGGER.error("aop failure", e);
}
}
private static Map<Class<?>, Set<Class<?>>> createProxyMap() throws Exception {
Map<Class<?>, Set<Class<?>>> proxyMap = new HashMap<Class<?>, Set<Class<?>>>();
addAspectProxy(proxyMap);
addTransactionProxy(proxyMap);
return proxyMap;
}
private static void addAspectProxy(Map<Class<?>, Set<Class<?>>> proxyMap) throws Exception {
Set<Class<?>> proxyClassSet = ClassHelper.getClassSetBySuper(AspectProxy.class);
for (Class<?> proxyClass : proxyClassSet) {
if (proxyClass.isAnnotationPresent(Aspect.class)) {
Aspect aspect = proxyClass.getAnnotation(Aspect.class);
Set<Class<?>> targetClassSet = createTargetClassSet(aspect);
proxyMap.put(proxyClass, targetClassSet);
}
}
}
private static void addTransactionProxy(Map<Class<?>, Set<Class<?>>> proxyMap) {
Set<Class<?>> serviceClassSet = ClassHelper.getClassSetByAnnotation(Service.class);
proxyMap.put(TransactionProxy.class, serviceClassSet);
}
private static Set<Class<?>> createTargetClassSet(Aspect aspect) throws Exception {
Set<Class<?>> targetClassSet = new HashSet<Class<?>>();
Class<? extends Annotation> annotation = aspect.value();
if (annotation != null && !annotation.equals(Aspect.class)) {
targetClassSet.addAll(ClassHelper.getClassSetByAnnotation(annotation));
}
return targetClassSet;
}
private static Map<Class<?>, List<Proxy>> createTargetMap(Map<Class<?>, Set<Class<?>>> proxyMap) throws Exception {
Map<Class<?>, List<Proxy>> targetMap = new HashMap<Class<?>, List<Proxy>>();
for (Map.Entry<Class<?>, Set<Class<?>>> proxyEntry : proxyMap.entrySet()) {
Class<?> proxyClass = proxyEntry.getKey();
Set<Class<?>> targetClassSet = proxyEntry.getValue();
for (Class<?> targetClass : targetClassSet) {
Proxy proxy = (Proxy) proxyClass.newInstance();
if (targetMap.containsKey(targetClass)) {
targetMap.get(targetClass).add(proxy);
} else {
List<Proxy> proxyList = new ArrayList<Proxy>();
proxyList.add(proxy);
targetMap.put(targetClass, proxyList);
}
}
}
return targetMap;
}
}
|
ProxyManager类生成最终代理类:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
public class ProxyManager {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static <T> T createProxy(final Class<?> targetClass, final List<Proxy> proxyList) {
return (T) Enhancer.create(targetClass, new MethodInterceptor() {
@Override
public Object intercept(Object targetObject, Method targetMethod, Object[] methodParams, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {
return new ProxyChain(targetClass, targetObject, targetMethod, methodProxy, methodParams, proxyList).doProxyChain();
}
});
}
}
|
提供代理模板类
我们需要暴露给用户如何使用aop,因此提供了代理模板类,里面提供了各种钩子函数供用户选择。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
|
public abstract class AspectProxy implements Proxy {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(AspectProxy.class);
@Override
public final Object doProxy(ProxyChain proxyChain) throws Throwable {
Object result = null;
Class<?> cls = proxyChain.getTargetClass();
Method method = proxyChain.getTargetMethod();
Object[] params = proxyChain.getMethodParams();
begin();
try {
if (intercept(cls, method, params)) {
before(cls, method, params);
result = proxyChain.doProxyChain();
after(cls, method, params, result);
} else {
result = proxyChain.doProxyChain();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("proxy failure", e);
error(cls, method, params, e);
throw e;
} finally {
end();
}
return result;
}
public void begin() {
}
public boolean intercept(Class<?> cls, Method method, Object[] params) throws Throwable {
return true;
}
public void before(Class<?> cls, Method method, Object[] params) throws Throwable {
}
public void after(Class<?> cls, Method method, Object[] params, Object result) throws Throwable {
}
public void error(Class<?> cls, Method method, Object[] params, Throwable e) {
}
public void end() {
}
}
|
其中proxy接口如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
public interface Proxy {
Object doProxy(ProxyChain proxyChain) throws Throwable;
}
|
值得注意的是AopHelper的初始化顺序,必须在BeanHelper初始化后,IocHelper初始化前初始化:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
public final class HelperLoader {
public static void init() {
Class<?>[] classList = {
ClassHelper.class,
BeanHelper.class,
AopHelper.class,
IocHelper.class,
ControllerHelper.class
};
for (Class<?> cls : classList) {
ClassUtil.loadClass(cls.getName());
}
}
}
|
以上就是aop的简单实现,我们可以通过注解@Aspect注解同时继承AspectProxy类来代理目标类,实现不侵入业务的逻辑。
实现dispatcherServlet
主要流程图
转发器实现接受请求并且将请求转发到对应的处理方法中,主要流程如下:

封装请求与处理器映射
我们要做的是封装请求与处理方法的映射,唯一标识一个请求的方法是请求路径与请求方法的组合,前面已经将controller加入bean容器中了,只需要解析controller中的Action注解并封装成映射即可。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
|
public final class ControllerHelper {
private static final Map<Request, Handler> ACTION_MAP = new HashMap<Request, Handler>();
static {
Set<Class<?>> controllerClassSet = ClassHelper.getControllerClassSet();
if (CollectionUtil.isNotEmpty(controllerClassSet)) {
for (Class<?> controllerClass : controllerClassSet) {
Method[] methods = controllerClass.getDeclaredMethods();
if (ArrayUtil.isNotEmpty(methods)) {
for (Method method : methods) {
if (method.isAnnotationPresent(Action.class)) {
Action action = method.getAnnotation(Action.class);
String mapping = action.value();
if (mapping.matches("\\w+:/\\w*")) {
String[] array = mapping.split(":");
if (ArrayUtil.isNotEmpty(array) && array.length == 2) {
String requestMethod = array[0];
String requestPath = array[1];
Request request = new Request(requestMethod, requestPath);
Handler handler = new Handler(controllerClass, method);
ACTION_MAP.put(request, handler);
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
public static Handler getHandler(String requestMethod, String requestPath) {
Request request = new Request(requestMethod, requestPath);
return ACTION_MAP.get(request);
}
}
|
封装请求参数
我们需要封装请求参数,并且从ACTION_MAP中获取对应的handler,反射调用即可
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
|
@WebServlet(urlPatterns = "/*", loadOnStartup = 0)
public class DispatcherServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
public void init(ServletConfig servletConfig) throws ServletException {
HelperLoader.init();
ServletContext servletContext = servletConfig.getServletContext();
registerServlet(servletContext);
UploadHelper.init(servletContext);
}
private void registerServlet(ServletContext servletContext) {
ServletRegistration jspServlet = servletContext.getServletRegistration("jsp");
jspServlet.addMapping("/index.jsp");
jspServlet.addMapping(ConfigHelper.getAppJspPath() + "*");
ServletRegistration defaultServlet = servletContext.getServletRegistration("default");
defaultServlet.addMapping("/favicon.ico");
defaultServlet.addMapping(ConfigHelper.getAppAssetPath() + "*");
}
@Override
public void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
ServletHelper.init(request, response);
try {
String requestMethod = request.getMethod().toLowerCase();
String requestPath = request.getPathInfo();
Handler handler = ControllerHelper.getHandler(requestMethod, requestPath);
if (handler != null) {
Class<?> controllerClass = handler.getControllerClass();
Object controllerBean = BeanHelper.getBean(controllerClass);
Param param;
if (UploadHelper.isMultipart(request)) {
param = UploadHelper.createParam(request);
} else {
param = RequestHelper.createParam(request);
}
Object result;
Method actionMethod = handler.getActionMethod();
if (param.isEmpty()) {
result = ReflectionUtil.invokeMethod(controllerBean, actionMethod);
} else {
result = ReflectionUtil.invokeMethod(controllerBean, actionMethod, param);
}
if (result instanceof View) {
handleViewResult((View) result, request, response);
} else if (result instanceof Data) {
handleDataResult((Data) result, response);
}
}
} finally {
ServletHelper.destroy();
}
}
}
|
解析处理器返回值
根据handler返回值判读即可:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
|
@WebServlet(urlPatterns = "/*", loadOnStartup = 0)
public class DispatcherServlet extends HttpServlet {
private void handleViewResult(View view, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException, ServletException {
String path = view.getPath();
if (StringUtil.isNotEmpty(path)) {
if (path.startsWith("/")) {
response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath() + path);
} else {
Map<String, Object> model = view.getModel();
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> entry : model.entrySet()) {
request.setAttribute(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
request.getRequestDispatcher(ConfigHelper.getAppJspPath() + path).forward(request, response);
}
}
}
private void handleDataResult(Data data, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
Object model = data.getModel();
if (model != null) {
response.setContentType("application/json");
response.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
PrintWriter writer = response.getWriter();
String json = JsonUtil.toJson(model);
writer.write(json);
writer.flush();
writer.close();
}
}
}
|
转发器的主要思想是拦截所有请求,并获取对应的处理器,解析处理器返回值,转发给客户端。
相关资料
- 源码地址:手写简易版spring框架
- 参考资料:架构探险从零开始写java web框架